

“sudo -i” sets the environment variables to match the targeted user’s profile, allowing the user to execute commands with the same permissions as if the user were the targeted account.ĥ. The “su” and “sudo su” only switch to the desired user account, while “sudo -s” and “sudo -i” can execute terminal commands with greater system-level authority.Ĥ. The “su” command and “sudo su” only switch to the desired user account without changing the environment variables or settings, while “sudo -s” and “sudo -i” provide an environment similar to that of the user with root access.ģ.
#SU VS SUDO SU PASSWORD#
The “su” command always requires the root password to execute, while “sudo su,” “sudo -s,” and “sudo -i” require the user’s password who is running the command.Ģ. Now, let’s talk about the differences between them.ġ. It is similar to “su -” but with the added security and authentication benefits of “sudo”, requiring the user’s password who is running the command.
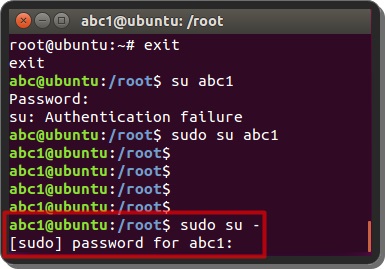
It provides you with access to that user’s environment, including their HOME directory. “sudo -i” is a way to log in as another user or to grant root access to execute several commands as if you were the root user. It does not require the root password instead, it requires the user’s password who is running the command.Ĥ. The command prompt changes to show that the user is now logged in as the other user. It is similar to the “su” command but is used when you don’t know the root password. “sudo -s” is a way to run a shell as another user, usually root. It prompts the user to enter their password before granting permission, which may or may not be the root password.ģ. It works by running su as root using sudo. It is a way to switch to another user account without logging out of the current user. The command always requires the root password to execute.Ģ. “su” stands for “switch user” or “substitute user.” It allows you to switch to another user account without logging out of the current one. So, what are the differences between su, sudo su, sudo -s, and sudo -i?ġ. Although they share some similarities, they serve different purposes, and using one instead of the other can cause unwanted results. As a Linux user, you must have come across at least one if not all four of these commands: su, sudo su, sudo -s, and sudo -i.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
